| CAS
NO. |
546-46-3
(Anhydrous)
5990-32-9 (Dihydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. |
208-901-2 |
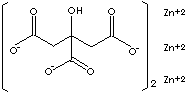
| FORMULA |
[OOCCH2C(OH)(COO)CH2COO]2Zn3 |
| MOL
WT. |
574.37 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2918.16 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral
rat LD50: > 5,000 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
2-hydroxy-1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, zinc salt;
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White
to yellow powder |
| MELTING POINT |
334
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
100 g/l |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Zinc is an essential mineral having a role in the maintenance of the body's
nervous and immune systems (T-cell function). This mineral is involved in the biochemical
reactions as an antioxidant in the healing process and develops normal tissues
Zinc is a cofactor in enzymatic reactions such as protein synthesis polymerases
and in carbonic acid anhydrase. Zinc maintains the body's alkaline balance. Zinc
finger, a structural domain found in many gene-regulatory proteins, is a
component of hydrophobic hormones acting stabilizing the biomembrane structures
and cell membrane metabolism. Zinc deficiencies may result in prolonged wound
healing, delayed sexual maturation, mental lethargy, skin changes, and
susceptibility to infections. Gluconate and citrate forms are mainly used as
zinc supplements. They are easily absorbed by the body. Zinc citrate can be formulated in pharmaceuticals, and
foods as a zinc supplement. Zinc citrate is used as an ingredient to treat
common cold and various hygienic products. Zinc inhibits the growth of
bacteria in the throat and can be used in toothpaste. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
White
to yellow powder |
|
CONTENT |
96.0%
min |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
Positive
(Test A,
B)
|
|
ZINC CONTENT |
31.0%
(Dihydrate) - 34.0% (Anhydrate)( |
|
SULFATE |
0.05% max |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
3.0%
max |
|
CADMIUM |
5ppm
max |
|
CHLORIDE |
0.05% max |
|
LEAD |
10ppm
max |
|
ARSENIC |
3ppm
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF CITRIC ACID
|
Citric Acid (2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid, in IUPAC naming) is a
colourless crystalline organic compound belong to carboxylic acid family. It
exists in all plants (especially in lemons and limes) and in many animal tissues
and fluids. In biochemistry, it is involved in important metabolism of almost
all living things; the Krebs cycle (also called citric acid cycle or
tricarboxylic acid cycle), a part of the process by which animals convert food
to energy. Citric acid works as a preservative ( or as an antioxidant) and
cleaning agent in nature. It is commercially obtained by fermentation process of
glucose with the aid of the mold Aspergillus niger and can be obtained
synthetically from acetone or glycerol. It can be used as an sour taste enhancer
in foods and soft drinks. The three carboxy groups lose protons in solution;
resulting in the excellent pH control as a buffer in acidic solutions. It is
used as a flavouring, stabilizing agent and acidulant (to control acidity) in
food industry, in metal-cleaning compositions as it chelates metals. Citric acid
is available in forms of anhydrous primarily and in monohydrate, the
crystallized form from water. The hydrated form will be converted to the
anhydrous form above 74 C. Citrate is a salt or ester of citric acid. Citrates
are formed by replacing the acidic one, two, or all three of the carboxylic
hydrogens in citric acid by metals or organic radicals to produce an extensive
series of salts, esters, and mixed (double) salts. Cirrates are used in food,
cosmetics, pharmaceutical and medicine industries as well as in plastic
industry; nutrient or food additives having functions of acidity regulator,
sequestering and stabilizing agent, antioxidants synergist, firming agent;
anticoagulant for stored whole blood and red cells and also for blood specimens
as citrates chelate metal ions and saline cathartics, effervescent medicines;
high boiling solvent, plasticizer and resin for food contact plastics.
|
